Osteochondrosis is a chronic disease that is symptomatic stated by dystrophic disorders in articular cartilage. It is usually occurred by spinal osteochondrosis, when changes occur in the intervertebral disc and the intervertebral joints. Depending on the localization, the cervical, thoracic and lumbar osteochondrosis are distinguished. Osteochondrosis is also often found, where all parts of the spine suffer. Pathology requires consultation with doctors and an integrated approach to treatment.

Information
Spinal diseases, like other chronic diseases, are quickly "younger". If the pain in the back and the joints is disturbing the elderly, today the patient is 18-30 years old to treat the doctor.
Scientists think that a prerequisite for the development of the disease, osteochondrosis is also facilitated by prolonged sitting position. In addition, with age, the articular cartilage loses elasticity and elasticity, thin; The intervertebral disc loses moisture and the ability to absorb the shock, becoming exposed during physical work.
Cause
The cause of cervical osteochondrosis lies in the load and they affect the cervical region under different conditions. In this regard, the muscles in the neck begin to decrease intensively, thus balancing this burden, resulting in cramps, as well as infringement of blood flow in this area.
- Violations of posture scoliosis, bends, back rounds, kyphosis and other posture disorders, though they are not essential, cause serious violations of the spinal column balance. As a result, the load on the intervertebral disc is distributed unevenly, causing their deformation and increasing wear. The vertebrae begins to close, causing the nerve process violation, the cervical osteochondrosis develops rapidly. The same consequences have a posture violation caused by changes in the natural position of the ribs.
- Muscle spasm spasmodic muscle reaction -back, breast, newspaper can lead to the fact that the individual part of the body is very tense. As a result, the general balance of the body is interrupted, causing a change in spinal position. Deformation can affect the cervical region or other parts of the spinal cord, causing chest, cervical, and lumbar osteochondrosis.
- Violation of blood supply, as the vertebrate does not have a direct connection to the blood circulatory system, they receive nutrition from the surrounding tissue. Violation of blood supply to the cervical spine leads to the fact that the disc does not receive enough fluid for rehydration (recovery of form due to moisture absorption), and cartilage renewal. As a result, their thirst is accelerated, there is a decrease in distances between the cervical region vertebra, leading to osteochondrosis.
- Violation of conservation, decreased nerve root sensitivity leads to pathological changes in their structure, as a result of displacement and deformation of the cervical regional vertebrae remains unknown to the patient. After all, pain is not present due to sensitivity.
- Internal organ disease is the wrong position of the internal organs, displacements and decreases as various dysfunction leads to general balance in the body. As a result, this affects the position of the spinal column - the cervix, the lumbar vertebrae is transferred and defective, leading to the corresponding type of osteochondrosis.

In general, osteochondrosis of the cervical region develops due to the effects of adverse external factors that violate the natural balance of the spinal column and other systems of the human body.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis of cervical osteochondrosis begins with the accumulation of all the necessary information about the patient. The specialist asked about complaints that harassed the person, interested in his professional activities, and how he spent his weekend. One important thing is the presence of osteochondrosis in parents, grandparents, as this is a hereditary disease.
Then the doctor proceeded directly to the patient's visual examination. He studied the cervical compartment and his back for posture curvature, penetrating the cervical region. This allows the specialist to assess the level of development of the disease, as in the case of advanced, palpation of the cervical area causes sharp pain.
When checking, you should pay attention:
- About the severity of cervical lordosis;
- shoulder height in the patient;
- possible asymmetry of supraclock area;
- possible neck asymmetry (for example, as a result of congenital pathology or sharp muscle cramps);
- Muscle condition -shoulder and upper limbs (for example, one muscle atrophy can indicate compression of the cervical spine);
- Chin location - the chin is normal should be located along the midline;
- Neck movements (bending, right and rotation and rotation).
Palpation is carried out in the early position of the patient:
- lying on the back;
- lying on the stomach;
- Sit in the chair.
Studies on the number of movements are also conducted. It is performed in the early position of the patient sitting on the chair (to prescribe another spine).
Differentiate the following basic movements in the cervical region:
- flexion;
- Advanced;
- slope to the right and left;
- Rotation.
About half of the volume and the extended volume occurs between the back of the head, the vertebra C1 and the C2. The rest of the movement is carried out due to the underlying vertebra, with a large scale of movement in the C5-C7 vertebra. Side tendencies are distributed evenly between all vertebrae.
To make the diagnosis accurately, additional studies are set:
- X -ray cervical region. This method is appropriate in the early stages of the disease, but it is not useful in advanced form.
- CT (Tomography is calculated). Allows you to see structural changes in the vertebra, but with the help of this method it is impossible to determine the size of the hernia between the vertebrae.
- MRI. It is considered the most effective method for diagnosing cervical osteochondrosis. You can determine the size of the hernia between the disc, as well as their developmental stages.
- Your doctor can also prescribe a duplex scan that allows you to determine a normal blood circulation in the artery.
Treatment
Treatment of cervical osteochondrosis is a complex therapy that includes taking drugs, gels, and various physiotherapy steps. An important role is played by therapeutic gymnastics, as well as massage area.
Remedy
It is not possible to eliminate the consequences of degenerative-dystrophic changes in the spine without using the drug. The use of medicines in the treatment of osteochondrosis of the cervical area is one of the main points of complex approach to healing, used by most traditional physicians.
It is designed to solve several problems, including:
- Stop symptoms of pain and eliminate inflammation;
- remove muscle cramps;
- stimulates the process of producing cartilage and cells -bone tissue;
- Strengthening the properties of the body, improving immunity;
- Improve general condition by eliminating other symptoms that interfere with recovery.
Depending on this purpose, all medications prescribed by doctors suffering from cervical osteochondrosis can be divided into the following groups:
- Analgesic (non -—steroid drug that relieves pain).
- Anti -inflammatory (steroids) is a hormone drug that relieves inflammation phenomena and, thereby eliminating pain.
- Chondroprotectors are drugs that contain substances that replace cartilage tissue components - chondroitin, hyaluronic acid.
- Musorelaxants. These are medicines that soothe muscle tone. They are used in surgery and orthopedic as an additional remedy to stop pain. Such medicines are administered by parents, and are therefore always under the supervision of a doctor.
- Vitamins. With osteochondrosis of the cervical area, vitamins are prescribed, affect the peripheral nervous system and increase conductivity. Water -soluble vitamins: B1, B6, B12, Fat -soluble vitamins: A, C, D, E. In recent years, combined drugs containing both painkillers and vitamin components more frequently.
- Ointment and gel for external use.

Physiotherapeutic
The main goal of physiotherapy treatment is to stimulate the process of regeneration in the body and eliminate pain. The most popular methods in the treatment of cervical chondrosis are as follows:
- Ultrasound. Physium with ultrasound waves is used to relieve serious manifestations of pain and inflammatory reactions. Ultrasound is a massage of neck tissue, after which metabolism is activated.
- Vibration massage. The effect on the area of the pain during the vibration sequence is through mechanical swinging. For proper physiotherapy behavior, strip vibrorser is commonly used.
- Electrophoresis. Methods of conducting physiotherapy care for cervical osteochondrosis are carried out using the current and modulated current, as well as electric fields when the body is administered into the drug tissue. Electrophoresis perfectly relieves spasmodic syndrome and relieves pain in inflamed muscles.
- Magnetotherapy. The core of magnetotherapy as a defect in the cervical area osteochondrosis is explained by the use of constant or variable field variables with magnets, different size frequency. This method can help the patient eliminate the pain and stop the inflammation in the fireplace. This procedure is often performed at home after acquiring special magnetographic devices.
- Dutoenzor-Tapapi. Currently, the physiotherapy method is relatively popular, which consists of stretching the spinal column under the patient's body mass. To carry out such procedures, mattresses organized in a special way are needed, which has tended to ribs and they change locations under their own weight. Muscle tone is normalized, leading to their relaxation.
- Laser therapy. Laser has a complex effect on the focus of inflammation, it activates the biological processes in the nervous system tissue. This allows you to get a positive effect on treatment. Complex effects on the body consist of anti -healing effects, analgesics and wounds. A laser treatment procedure should not exceed 15 minutes. This is the optimum time of exposure to helic laser sector in affected areas. In this case, the laser period in one pain should not exceed 2 minutes.
- Balneotherapy. The benefits of mineral water have been known for a long time, this is based on balneotherapy. This procedure implies the use of active water sources in the treatment of osteochondrosis. In addition to the use of baths, various types of souls and active swimming in the pool, therapy involves the use of therapeutic mud applications to painful areas. Therapeutic effects are achieved with simultaneous effects of chemical active ingredients contained in water at various temperature conditions. This technique allows you to stop the pain syndrome by improving the local micro circulation in the tissue.
Exercise therapy
Keep in mind that exercise therapy is not performed when the signs of anxiety begin: pain. After the LFK complex, they can improve and cause difficulties.
There are several general suggestions for charging:
- Physical education should take place indoors with good ventilation, a great choice on the street.
- Classes are performed only during the disease period (when there are no symptoms).
- Exercise therapy should be broad, not embarrassing movement and breathing.
- All movements are smooth, the amplitude and the number of repetitions gradually increase.
- If the pain starts, you should immediately stop the lesson.
- Lead the class and end the measurement of pressure and pulse. When these indications are different from normal, the load should be reduced.
- It is advisable to hear your breathing throughout the lesson, this will improve efficiency. All stretch exercises are done on breathing.
- It is very important to gradually increase the burden and the number of repetitions, this will reduce the risk of injury and prevent hard work.
- Training is important to do regularly, so you can achieve fast results.
- Before starting a free class, you should consult your doctor and agree with a set of exercises.
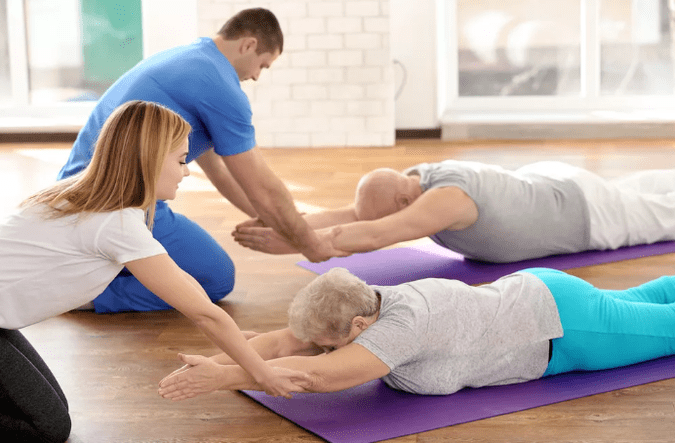

Recommended training in the starting position located in the abdomen:
- The head is at the end of the forehead, the back of the head, the elbow parallel to the floor. Raise your head with your hands off the floor, hold this position to 4 accounts, lower and rest. Repeat 2-4 times.
- The head stopped on the chin, the palm of the hand under the chin. Time in time, stretch your arm forward, two - spread to the side, three - stretch forward, four - starting position. Repeat 2-4 times.
- Hands are extended forward. Swimming the "rabbit" style, repeated 4-8 times.
- Palm under the chin, emphasis on the palm of your forehead. Often, take the back heel. Repeat 4-8 times.
The recommended training is in the starting position on the side (on the right, then on the left):
- The right hand is extended, the right ear is located above it, lift the right hand with your head, hold the 4th account, lower and rest. Repeat 2-4 times.
- The left hand is located on the floor in front of the chest, the left foot makes the movements fly back and so on. Repeat 6-8 times.
- Left hand along the body, raising the left hand and exiting, lower, lower. Repeat 2-4 times.
- Left hand in the thigh. Attract both knees to the chest in your breath, straighten your feet on inspiration. Repeat the training 2-4 times.